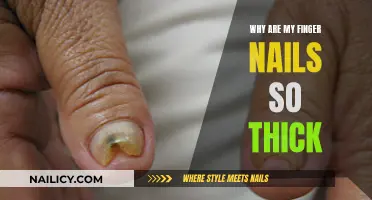
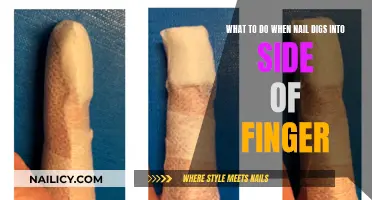
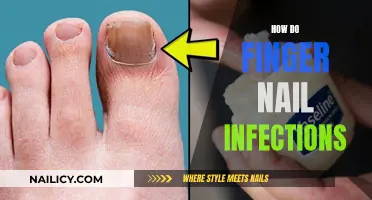
Many people have the habit of picking at their fingernails, often without realizing it. This behavior can be a source of anxiety and discomfort, as it can lead to damaged nails and skin around the nails. Understanding the reasons behind this habit can help individuals address the issue. Some common triggers include stress, boredom, anxiety, or a desire to feel something tactile. Others may pick their nails as a way to cope with emotional distress or to seek a temporary release of tension. Recognizing the underlying causes is the first step toward breaking this habit and promoting healthier nail care practices.
What You'll Learn
- Psychological Factors: Boredom, stress, anxiety, or a need for sensory stimulation
- Habit Formation: Repetitive behavior can become a habit, triggered by routine or environment
- Social Influences: Peer pressure, social norms, or media influence may encourage nail-biting
- Emotional Regulation: Some bite nails to cope with emotions, providing a temporary release of tension
- Attention-Seeking: Seeking attention or focus, especially in stressful or boring situations

Psychological Factors: Boredom, stress, anxiety, or a need for sensory stimulation
The act of nail-biting or picking at the nails is a common behavior that can be influenced by various psychological factors, particularly when individuals are seeking ways to cope with boredom, stress, anxiety, or the need for sensory stimulation. These psychological triggers often play a significant role in understanding why someone engages in this habit.
Boredom is a common state that can lead to nail-biting. When individuals are bored, they may seek any available outlet to fill the void. Nail-biting can provide a temporary distraction and a way to channel nervous energy. For example, a student waiting for test results or an office worker with a slow workday might find themselves biting their nails as a passive-aggressive response to the monotony of their environment. This behavior often starts as a mild habit but can become more frequent and intense over time.
Stress is another significant psychological factor. When people feel overwhelmed, they may resort to nail-biting as a coping mechanism. It provides a physical outlet for the tension and anxiety they are experiencing. For instance, a person preparing for a major presentation or dealing with a heavy workload might find themselves unconsciously picking at their nails as a way to release stress. This behavior can be especially prevalent among students during exam periods or professionals facing high-pressure situations.
Anxiety disorders are also closely linked to nail-biting. Individuals with anxiety may engage in this habit as a form of self-soothing or as a way to gain a sense of control in their lives. For those with social anxiety, nail-biting can be a discreet way to occupy their hands and mind, reducing the discomfort of social interactions. Similarly, individuals with generalized anxiety may use this behavior to channel their nervous energy, providing a temporary relief from the constant worry and tension.
The need for sensory stimulation is another psychological factor. Some people may engage in nail-biting as a way to satisfy a craving for tactile sensations. The act of biting, scratching, or pulling at the nails can provide a unique sensory experience, which might be comforting or even addictive. This behavior can be particularly prevalent among individuals who have a higher sensitivity to touch or those who seek out various sensory experiences to satisfy their need for stimulation.
Understanding these psychological factors can help individuals recognize the underlying causes of their nail-biting habits. By identifying these triggers, one can develop strategies to manage boredom, stress, anxiety, and the need for sensory stimulation in healthier ways, ultimately reducing the urge to pick at their nails.
Unraveling the Mystery: Why Do Finger Nails Peel?
You may want to see also

Habit Formation: Repetitive behavior can become a habit, triggered by routine or environment
The act of nail-biting, or onychophagia, is a common habit that many people struggle with, often without even realizing it. This repetitive behavior can become a deeply ingrained habit, triggered by various factors such as routine, stress, or environmental cues. Understanding the underlying causes and the process of habit formation can be crucial in breaking free from this habit.
Habit formation is a fascinating psychological process. When an action is repeated consistently, especially in a specific context or routine, it creates a powerful association in the brain. The brain, being an incredibly adaptive organ, learns to anticipate and respond to these cues, often unconsciously. For example, a person might bite their nails when feeling anxious or bored, and over time, the act of biting becomes a go-to response to these emotions. This is because the brain has learned to associate the action with relief or distraction from the triggering emotion.
The environment plays a significant role in habit formation. Certain settings or situations can act as powerful triggers for repetitive behaviors. For instance, a person might find themselves biting their nails more frequently during work breaks, especially if their job is stressful or monotonous. The office environment, with its specific sounds, sights, and feelings, becomes a context that cues the nail-biting habit. Similarly, a person might develop a habit of picking at their cuticles while watching TV, as the activity becomes a comforting ritual during leisure time.
Routine is another critical factor in the development of habits. Daily routines provide structure and predictability, and they can influence the likelihood of engaging in certain behaviors. For example, a person might bite their nails as a way to pass time during a boring meeting, and over time, this behavior becomes a regular part of their work routine. Similarly, a student might develop a habit of picking at their nails while studying, especially if they find the subject matter challenging or uninteresting. The routine of studying, coupled with the desire to cope with stress or boredom, reinforces the habit.
Breaking a habit like nail-biting requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying triggers. One effective strategy is to become more mindful of the habit. Pay attention to the situations, emotions, and routines that consistently lead to nail-biting. By recognizing these patterns, you can start to develop alternative, healthier responses. For instance, when feeling anxious, you could try deep breathing exercises or squeezing a stress ball instead. Over time, as the new behaviors become more automatic, the old habit will gradually diminish.
Purple Nail Mystery: Unraveling the Unexpected Color Change
You may want to see also

Social Influences: Peer pressure, social norms, or media influence may encourage nail-biting
The social environment we inhabit can significantly impact our behaviors, and nail-biting is no exception. Peer pressure, social norms, and media influence are powerful forces that can encourage and perpetuate this habit. Understanding these social influences is crucial in addressing and overcoming this issue.
Peer pressure is a significant factor, especially during adolescence and early adulthood. When individuals are surrounded by friends or peers who engage in nail-biting, they may feel compelled to follow suit. This is often driven by the desire to fit in and be accepted by the group. For example, a teenager might start biting their nails after noticing that several of their friends do the same, hoping to gain social approval and avoid potential ridicule. The fear of being different or standing out can be a powerful motivator for maintaining this behavior.
Social norms play a role in shaping behaviors, including nail-biting. Certain cultures or social groups may have unspoken rules or traditions that involve nail-biting. For instance, in some societies, it is customary for children to bite their nails as a sign of nervousness or excitement. Over time, this behavior becomes normalized, and individuals may continue the habit without even realizing it. Media, including movies, television shows, and social media, can also reinforce these social norms. Seeing characters or influencers biting their nails in popular media can unconsciously encourage viewers to adopt the same behavior.
Media influence is another critical aspect to consider. The portrayal of nail-biting in movies, TV shows, and social media platforms can normalize the habit. For instance, a character in a popular teen drama might be shown biting their nails during moments of stress or anxiety, leading young viewers to mimic the behavior. Additionally, social media influencers, who often have a significant following, may inadvertently promote nail-biting by showcasing it as a trendy or fashionable habit. The desire to emulate these influencers can be particularly strong among impressionable youth.
To address nail-biting, it is essential to recognize these social influences and their potential impact. Breaking the habit may require a multi-faceted approach, including raising awareness about the social pressures at play, encouraging open conversations about the issue, and promoting healthier alternatives to cope with stress or anxiety. By understanding the social factors that contribute to nail-biting, individuals can make informed decisions and seek support to overcome this habit.
Bare Finger: Unveiling the Hidden Texture Beneath the Nail
You may want to see also

Emotional Regulation: Some bite nails to cope with emotions, providing a temporary release of tension
For many individuals, nail-biting is a complex behavior that often stems from emotional regulation and stress management. It is a common coping mechanism that provides a temporary release of tension and anxiety. When faced with overwhelming emotions or stressful situations, some people find solace in the repetitive action of biting their nails. This behavior can be a way to channel and release pent-up emotions, especially when other outlets are not readily available or socially acceptable.
The act of biting one's nails can be a self-soothing technique, offering a sense of comfort and control in an otherwise chaotic or uncertain environment. For example, a student preparing for exams might find themselves biting their nails as a response to the pressure and stress of academic demands. Similarly, someone facing a challenging work project or personal conflict might resort to nail-biting as a means to calm their nerves and distract themselves from the source of their anxiety.
This emotional regulation strategy is often unconscious and can be a result of learned behavior. Individuals may have developed this habit during childhood as a response to stress or as a way to seek comfort from caregivers. Over time, the action becomes a familiar and seemingly effective way to manage emotions, even though it may not provide long-term solutions to the underlying issues.
It is important to recognize that while nail-biting can offer temporary relief, it is generally not a healthy or productive way to cope with emotions. The habit can lead to various physical and social consequences, such as damaged nails, bad breath, and social embarrassment. Moreover, it may indicate the presence of deeper emotional or psychological concerns that require professional attention.
Understanding the emotional triggers behind nail-biting can be a crucial step in breaking the habit. By identifying the specific emotions or situations that prompt this behavior, individuals can explore healthier alternatives for emotional regulation. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, mindfulness meditation, or engaging in creative outlets can provide more constructive ways to manage stress and emotions, ultimately reducing the urge to bite one's nails.
Mastering the Art of Nail Painting: Essential Tips for the Perfect Base
You may want to see also

Attention-Seeking: Seeking attention or focus, especially in stressful or boring situations
The act of nail-biting or picking at one's nails is a common behavior that often serves as a coping mechanism or a way to seek attention, especially in stressful or monotonous situations. This behavior can be a result of an individual's desire to gain focus and engagement, particularly when they are in environments that may be perceived as dull or challenging. For many, picking at their nails provides a temporary distraction and a release of tension, allowing them to momentarily escape the pressures or monotony of their surroundings.
In stressful situations, engaging in nail-biting can be a way to channel nervous energy into a seemingly harmless activity. It provides a physical outlet for the anxiety or tension one might feel, offering a sense of control and a temporary distraction from the source of stress. This behavior can become a habitual response, especially if it has been used as a coping strategy for a prolonged period.
On the other hand, in boring or unstimulating environments, nail-biting can be a means to seek attention and engagement. When individuals are in situations where they feel overlooked or unentertained, this behavior can be a way to draw attention to themselves and create a sense of involvement. It might be a subconscious attempt to communicate a need for interaction or a desire to be noticed.
Understanding the underlying reasons for this behavior is crucial in addressing it effectively. For those who struggle with nail-biting, especially in stressful or boring contexts, recognizing the triggers and the emotional or environmental factors at play can be the first step towards change. This awareness can empower individuals to find alternative, healthier ways to manage stress, seek attention, or cope with boredom, ultimately leading to improved well-being and a reduction in the urge to pick at their nails.
Unraveling the Mystery: When Your Finger Nails Turn Pink
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Nail-biting or picking is a common habit that can have various underlying causes. It might be a stress-relieving mechanism, a way to cope with anxiety or boredom, or even a habitual response to certain textures or sensations. Sometimes, it can be a result of nutritional deficiencies or an underlying condition like obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Identifying the root cause can help you find effective strategies to manage and stop this behavior.
Breaking the habit of nail-biting can be challenging, but several strategies can help. Try to identify triggers and find alternative ways to manage stress or boredom, such as taking a short walk, practicing deep breathing exercises, or engaging in a hobby. Keep your nails trimmed and filed to reduce the urge to bite, and consider using nail covers or wraps to provide a physical barrier. If the habit persists, seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor can provide valuable support and guidance.
Yes, there are potential health risks and complications associated with frequent nail-biting. It can lead to infections, especially if you bite your nails and then touch your face, as bacteria and germs can enter the body through breaks in the skin. Additionally, it may cause damage to the nail bed, resulting in pain, bleeding, and even permanent deformities. In some cases, it can also lead to a condition called 'onychocryptosis,' where the nail grows into the skin, causing pain and discomfort.