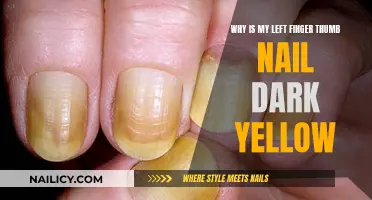
Nail infections can be caused by injury, bacteria, viruses, fungi, and skin diseases. Bacterial paronychia is one of the most common hand infections and is usually caused by skin irritation or injury. Fungal nail infections occur when a fungus attacks a fingernail, toenail, or the skin under the nail. Symptoms vary depending on the type of infection and can include white or yellow spots under the nail, which can spread and turn the nail white, yellow, green, or black.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Cause | Fungus, injury, skin diseases, bacteria, viruses, diabetes, weakened immune system |
| Symptoms | White or yellow spot under the nail, nail thickening, nail curling, nail loosening, nail bed redness, swollen skin, pain, warmth, tenderness, sudden appearance |
| Treatment | Nail care advice, personal hygiene, protective gloves, avoiding harsh chemicals, nail polish, home manicures, nail clippers |
| Risk Factors | Diabetes, weakened immune system, age, injury, skin diseases |
| Complications | Nail damage, bone involvement, chronic paronychia |
What You'll Learn
- Fungal nail infections occur when a fungus attacks a fingernail or skin under the nail
- Bacterial paronychia appears suddenly when the skin around the nail is irritated or injured
- Paronychia can be caused by injury, infection or skin diseases
- Good hygiene and nail care can prevent nail infections
- Kids with diabetes have a higher chance of getting paronychia infections

Fungal nail infections occur when a fungus attacks a fingernail or skin under the nail
A fungal nail infection occurs when a fungus attacks a fingernail, a toenail, or the skin under the nail, called the nail bed. Symptoms are different, depending on which type of fungal nail infection you have. They usually start mild and get more serious. At first, you may only see a white or yellow spot under your nail. Over time, this spreads and can turn your whole nail white, yellow, green, or black. The nail may thicken and could be hard to trim. It may start to curl up or down or loosen from the nail bed.
People with diabetes or compromised immune systems have a higher risk of fungal nail infections. Toenail problems tend to be more common among older people. Fingernail infections usually respond faster to treatment than toenail infections. Some conditions need professional treatment from a doctor or a dermatologist.
Common causes of nail problems include injury, infection and skin diseases such as eczema and psoriasis. When skin gets damaged, germs can get in and cause an infection. These germs can be:
- Bacteria
- Viruses
- Fungi
Some people get more than one infection, or the infection comes back after treatment (chronic paronychia). Untreated, the infection can cause damage to the nail. Rarely, untreated paronychia can go deeper into the finger or toe and lead to a serious infection. The infection may progress to involve the underlying bone.
Treatment may include advice on appropriate nail care. Practice good personal hygiene. Wear protective gloves for wet jobs such as washing the dishes. Avoid harsh chemicals such as strong soaps and detergents. Avoid or limit the handling of chemicals such as hair dyes. Take care with the use of nail polish. Don’t clean under your nails too often or too aggressively. When giving yourself a home manicure, do not push back the cuticles. Resist the urge to bite or tear off hangnails – use nail clippers.
Curved Index Nail: Unraveling the Mystery Beneath the Tip
You may want to see also

Bacterial paronychia appears suddenly when the skin around the nail is irritated or injured
Bacterial paronychia is a nail infection that appears suddenly when the skin around the nail is irritated or injured. When the skin gets damaged, germs can get in and cause an infection. These germs can be bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
The skin around the nail is irritated or injured by injury, infection, or skin diseases such as eczema and psoriasis. Kids with diabetes also have a higher chance of getting paronychia infections. If your child has paronychia, it's usually easy to recognize. Look for: an area of red, swollen skin around a nail that's painful, warm, and tender to the touch.
Bacterial paronychia usually appears very suddenly. Some people get more than one infection, or the infection comes back after treatment (chronic paronychia). Untreated, the infection can cause damage to the nail. Rarely, untreated paronychia can go deeper into the finger or toe and lead to a serious infection. The infection may progress to involve the underlying bone.
Fingernail infections usually respond faster to treatment than toenail infections. Depending on the cause, treatment may include:
- Advice on appropriate nail care.
- Practice good personal hygiene.
- Wear protective gloves for wet jobs such as washing the dishes.
- Avoid harsh chemicals such as strong soaps and detergents.
- Avoid or limit the handling of chemicals such as hair dyes.
- Take care with the use of nail polish.
- Don’t clean under your nails too often or too aggressively.
- When giving yourself a home manicure, do not push back the cuticles.
- Resist the urge to bite or tear off hangnails – use nail clippers.
Nail Splitting: Understanding the Causes and Getting Relief
You may want to see also

Paronychia can be caused by injury, infection or skin diseases
Paronychia is a nail infection that occurs when the skin around the nail is irritated or injured. When the skin is damaged, germs can get in and cause an infection. These germs can be bacteria or fungi.
Paronychia is one of the most common hand infections. It usually happens when the skin around the nail is irritated or injured. When skin gets damaged like this, germs can get in and cause an infection. These germs can be:
- Bacteria
- Fungi
Kids with diabetes also have a higher chance of getting paronychia infections. If your child has paronychia, it's usually easy to recognize. Look for:
- An area of red, swollen skin around a nail that's painful, warm, and tender to the touch
- Bacterial paronychia usually appears very suddenly.
Toenail problems tend to be more common among older people. Fingernail infections usually respond faster to treatment than toenail infections. Depending on the cause, treatment may include:
- Advice on appropriate nail care
- Practice good personal hygiene
- Wear protective gloves for wet jobs such as washing the dishes
- Avoid harsh chemicals such as strong soaps and detergents
- Avoid or limit the handling of chemicals such as hair dyes
- Take care with the use of nail polish
- Don’t clean under your nails too often or too aggressively
- When giving yourself a home manicure, do not push back the cuticles
- Resist the urge to bite or tear off hangnails – use nail clippers
Hand, Foot, and Mouth: Unraveling the Mystery of Nail Lift
You may want to see also

Good hygiene and nail care can prevent nail infections
- Bacteria
- Fungus
- Viruses
Kids with diabetes also have a higher chance of getting paronychia infections. If your child has paronychia, it's usually easy to recognize. Look for an area of red, swollen skin around a nail that's painful, warm, and tender to the touch. Bacterial paronychia usually appears very suddenly.
Some people get more than one infection, or the infection comes back after treatment (chronic paronychia). Untreated, the infection can cause damage to the nail. Rarely, untreated paronychia can go deeper into the finger or toe and lead to a serious infection. The infection may progress to involve the underlying bone.
To prevent nail infections, wear protective gloves for wet jobs such as washing the dishes. Avoid harsh chemicals such as strong soaps and detergents. Avoid or limit the handling of chemicals such as hair dyes. Take care with the use of nail polish. Don’t clean under your nails too often or too aggressively. When giving yourself a home manicure, do not push back the cuticles. Resist the urge to bite or tear off hangnails – use nail clippers.
Unraveling the Mystery: Why Do Our Fingernails Accumulate So Much Dirt?
You may want to see also

Kids with diabetes have a higher chance of getting paronychia infections
Paronychia is a nail infection that occurs when the skin around the nail is irritated or injured. When the skin is damaged, germs can get in and cause an infection. These germs can be bacteria or fungi. Kids with diabetes also have a higher chance of getting paronychia infections. If your child has paronychia, it's usually easy to recognize. Look for: an area of red, swollen skin around a nail that's painful, warm, and tender to the touch. Bacterial paronychia usually appears very suddenly.
Nails support and protect the sensitive tips of our fingers and toes. Common causes of nail problems include injury, infection and skin diseases such as eczema and psoriasis. Some conditions need professional treatment from a doctor or a dermatologist. People with diabetes or compromised immune systems have a higher risk of fungal nail infections. Toenail problems tend to be more common among older people.
Fingernail infections usually respond faster to treatment than toenail infections. Depending on the cause, treatment may include: advice on appropriate nail care, practice good personal hygiene, wear protective gloves for wet jobs such as washing the dishes, avoid harsh chemicals such as strong soaps and detergents, avoid or limit the handling of chemicals such as hair dyes, take care with the use of nail polish, don’t clean under your nails too often or too aggressively, when giving yourself a home manicure, do not push back the cuticles, resist the urge to bite or tear off hangnails – use nail clippers.
The Surprising Nail Diversity in Mammals: Uncovering Hidden Patterns
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Symptoms of a finger nail infection are different depending on the type of infection. At first, you may only see a white or yellow spot under your nail. Over time, this spreads and can turn your whole nail white, yellow, green, or black. The nail may thicken and could be hard to trim. It may start to curl up or down or loosen from the nail bed.
Common causes of nail problems include injury, infection and skin diseases such as eczema and psoriasis. Kids with diabetes also have a higher chance of getting paronychia infections.
Fingernail infections usually respond faster to treatment than toenail infections. Treatment may include advice on appropriate nail care, practice good personal hygiene, wear protective gloves for wet jobs, avoid harsh chemicals, avoid or limit the handling of chemicals such as hair dyes, take care with the use of nail polish, don't clean under your nails too often or too aggressively, and do not push back the cuticles.