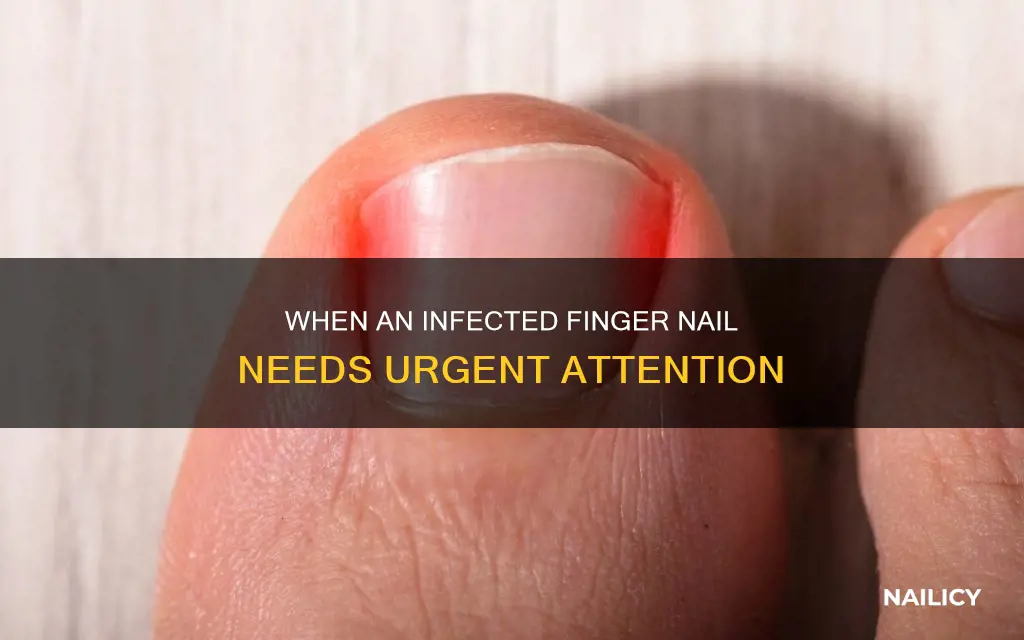
An infected fingernail, while often a minor inconvenience, can sometimes indicate a more serious underlying condition. It's important to recognize when an infected nail is a cause for concern and requires immediate medical attention. In this paragraph, we will explore the potential severity of nail infections and discuss the signs that may indicate a more serious issue, such as a bacterial or fungal infection that has spread beyond the nail bed. Understanding these indicators can help individuals take appropriate action to prevent further complications and ensure timely treatment.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Symptoms | Redness, swelling, pain, warmth, and discharge from the nail bed. Fever, chills, and fatigue may also be present. |
| Causes | Bacterial or fungal infections, often due to poor hygiene, cuts or injuries, or underlying health conditions. |
| Risk Factors | Diabetes, weakened immune system, poor circulation, and certain medications. |
| Complications | If left untreated, the infection can spread to the surrounding tissues, bones, or bloodstream, leading to serious health issues. |
| Treatment | Antibiotics or antifungal medications, proper nail care, and in severe cases, surgical intervention. |
| Prevention | Maintaining good hygiene, promptly treating nail injuries, and seeking medical advice for persistent or severe symptoms. |
What You'll Learn
- Infection Spread: Bacteria can travel from the nail bed to other parts of the body, causing serious infections
- Abscess Formation: Pus-filled bumps under the nail can indicate a severe bacterial infection
- Nail Detachment: Severe infections may lead to the nail separating from the nail bed
- Systemic Symptoms: High fever, chills, and fatigue can signal a serious infection affecting the entire body
- Delay in Treatment: Prolonged nail infections can lead to permanent nail damage and chronic pain

Infection Spread: Bacteria can travel from the nail bed to other parts of the body, causing serious infections
Infected finger nails, while often an uncomfortable and unsightly issue, can sometimes lead to more serious health concerns if left untreated. One of the primary reasons for this is the potential for bacterial infection to spread beyond the nail bed. The nail bed, being a warm and moist environment, provides an ideal breeding ground for bacteria. When an infection takes hold, it can quickly become a systemic issue, affecting not only the nail itself but also other parts of the body.
Bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus, can easily travel through the bloodstream from the nail bed. This is particularly concerning as these bacteria can cause a range of severe infections. For instance, they can lead to cellulitis, an infection of the skin and underlying tissue, which often presents as redness, swelling, and pain around the affected area. In more serious cases, the bacteria can enter the bloodstream and cause sepsis, a life-threatening condition characterized by a severe immune response to infection.
The risk of bacterial spread is especially high if the infection is left untreated or if it is caused by a resistant strain of bacteria. Proper hygiene and timely treatment are crucial in preventing the progression of nail infections. If you suspect you have an infected nail, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. A healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment, which may include antibiotics, antifungal medications, or even surgical intervention in severe cases.
In addition to the physical discomfort and potential for serious health complications, an infected nail can also have social and psychological impacts. It may lead to self-consciousness, especially if the infection is visible or causes deformity. Therefore, it is important to address the issue promptly to prevent both physical and emotional distress.
To minimize the risk of infection spread, it is advisable to maintain good nail hygiene. This includes keeping your nails clean and dry, trimming them regularly, and avoiding sharing personal items like nail clippers or towels. If you notice any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge, seek medical advice immediately. Early intervention can significantly reduce the risk of the infection spreading and causing more serious health issues.
Unraveling the Mystery: What Your Rippled Nails Might Tell You
You may want to see also

Abscess Formation: Pus-filled bumps under the nail can indicate a severe bacterial infection
An infected finger nail can be a serious medical concern, especially when it leads to the formation of an abscess. Abscesses are essentially localized collections of pus, which can develop under the nail or even within the nail bed. This condition is a clear indication of a severe bacterial infection and requires immediate attention to prevent further complications.
The presence of pus-filled bumps under the nail is a visible sign of an abscess. These bumps are often tender and may cause significant discomfort. When an infection reaches this stage, it has typically progressed beyond a simple nail infection and can affect the surrounding tissues, including the skin, soft tissues, and even the bone. The bacteria responsible for the infection can spread rapidly, making it crucial to address the issue promptly.
In many cases, an abscess under the nail is a result of a minor injury or trauma to the nail, which allows bacteria to enter and establish an infection. However, it can also occur without an obvious cause, especially if the individual has a weakened immune system or pre-existing conditions that make them more susceptible to infections. Diabetes, for example, can contribute to poor blood circulation and impaired wound healing, making nail infections more likely to progress to abscess formation.
If left untreated, the abscess may continue to grow, causing the nail to lift away from the nail bed. This can lead to further complications, such as the spread of infection to other parts of the body, bone infection (osteomyelitis), or even sepsis, a life-threatening condition. Therefore, it is essential to seek medical attention at the first sign of a serious nail infection to prevent the development of an abscess.
Treatment for abscess formation typically involves draining the pus under local anesthesia. This procedure can be performed in a doctor's office or clinic. After drainage, the area is carefully cleaned and dressed to promote healing. Antibiotic therapy is also necessary to address the bacterial infection and prevent its recurrence. Proper care and follow-up are crucial to ensure the infection is fully resolved and to reduce the risk of future complications.
Unveiling the Mystery: Jakcom Smart Finger Nail's Revolutionary Features
You may want to see also

Nail Detachment: Severe infections may lead to the nail separating from the nail bed
Infected finger nails can be a painful and concerning issue, and while many cases can be managed at home, there are situations where seeking medical attention is crucial. One potential complication that requires immediate care is nail detachment, which occurs when a severe infection reaches the nail bed and causes the nail to separate from its underlying structure. This condition is more serious than a simple fungal infection and can lead to further health complications if left untreated.
Nail detachment is often a result of a bacterial or fungal infection that has progressed and affected the nail matrix and surrounding tissues. When an infection is severe, it can cause inflammation and damage to the nail bed, leading to the nail becoming loose and potentially falling off. This is a more advanced stage of nail infection and should not be ignored. Symptoms may include intense pain, redness, and swelling around the affected nail, and the nail itself might appear discolored, thickened, or distorted.
If you suspect you have a severe nail infection leading to detachment, it is essential to act promptly. Here are some steps to take: First, wash the area with warm water and soap to clean the wound. Apply an antibiotic ointment to prevent further infection. Elevate the finger to reduce swelling. Avoid any pressure or trauma to the nail. In more severe cases, a doctor might need to be consulted. They may prescribe oral antibiotics, perform a minor surgical procedure to remove the infected portion of the nail, or even permanently remove the nail if the infection is extensive and recurrent.
Preventing nail infections is always better than treating them. Maintaining good foot and hand hygiene, keeping nails short and clean, and promptly treating any cuts or injuries to the nail bed can help reduce the risk of severe infections. However, if you notice any signs of a serious nail infection, such as increased pain, fever, or rapid spread of redness and swelling, it is crucial to seek medical advice without delay.
In summary, nail detachment is a serious consequence of untreated severe nail infections. It requires prompt medical attention to prevent further complications. Being aware of the signs and taking appropriate measures can help manage and treat such infections effectively.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Unique Nail Art with Different Fingers
You may want to see also

Systemic Symptoms: High fever, chills, and fatigue can signal a serious infection affecting the entire body
When an infected finger nail becomes a serious concern, it's important to recognize the signs that indicate a potential systemic infection. One of the most alarming indicators is the presence of high fever, chills, and fatigue. These systemic symptoms should never be ignored, as they suggest that the infection has progressed beyond the localized nail and is now affecting the body as a whole.
High fever is a classic sign of an infection, as the body's temperature rises in response to the invading pathogens. Chills often accompany the fever, causing shivering and a feeling of being cold, even in a warm environment. These symptoms are the body's attempt to fight off the infection, but they can be extremely uncomfortable and may indicate a severe underlying issue.
Fatigue, another systemic symptom, is a persistent feeling of tiredness and lack of energy. It can be overwhelming and may make even simple tasks seem exhausting. This fatigue is not just about feeling tired after a hard day's work; it is a sign that the body is under significant stress due to the infection. When an infected finger nail leads to high fever, chills, and fatigue, it suggests that the infection has spread to the bloodstream or other organs, requiring immediate medical attention.
In such cases, it is crucial to seek medical help promptly. A healthcare professional can assess the severity of the infection and provide appropriate treatment. This may include antibiotics to combat the infection, especially if it has reached a systemic level. Delaying treatment can lead to further complications and potentially serious health issues.
Recognizing these systemic symptoms is vital for timely intervention. If you or someone you know experiences a high fever, chills, and fatigue along with an infected finger nail, it is a strong indicator of a more serious infection. Taking immediate action can prevent the condition from worsening and ensure a faster recovery. Remember, when in doubt, always consult a medical professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
The Symbolism of Ring Finger Nail Color: Unlocking Hidden Meanings
You may want to see also

Delay in Treatment: Prolonged nail infections can lead to permanent nail damage and chronic pain
Nail infections, while often an inconvenience, can become a serious medical concern if left untreated for an extended period. The human body has a natural defense mechanism to fight off infections, but when it comes to the nails, this process can be hindered due to the nail's hard and protective nature. Over time, a minor fungal or bacterial infection can progress and lead to severe complications.
One of the primary reasons for the seriousness of delayed treatment is the potential for permanent nail damage. When an infection goes untreated, it can cause the nail to become thickened, discolored, and distorted. In severe cases, the infection may spread beneath the nail bed, leading to pain, swelling, and even the separation of the nail from the underlying tissue. This separation can result in the nail becoming fragile and prone to breaking or crumbling, often requiring medical intervention to restore its health.
Furthermore, prolonged nail infections can give rise to chronic pain, which may persist long after the initial infection has been treated. The infection can affect the surrounding tissues, including the skin and soft tissues around the nail, causing ongoing discomfort and sensitivity. This chronic pain can significantly impact an individual's quality of life, making everyday activities, such as typing, writing, or even wearing shoes, extremely difficult and painful.
In some cases, if the infection reaches the bloodstream or affects the nearby tissues severely, it can lead to more critical health issues. For instance, a severe nail infection can cause septic arthritis, an infection of the joint, which may require immediate medical attention and potentially surgical intervention. Therefore, it is crucial to recognize the signs of a nail infection and seek appropriate treatment to prevent such complications.
To avoid these serious consequences, it is essential to act promptly at the first sign of a nail infection. Simple measures like keeping the nails clean and dry, using antifungal creams or oral medications as prescribed, and maintaining good overall hygiene can help manage and treat nail infections effectively. Seeking professional medical advice is recommended to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment, especially if the infection persists or worsens over time.
Unveiling the Mystery: No Moons on Nails, Health Alert!
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
An infected finger nail, also known as onychomycosis, can be a serious issue if left untreated. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent pain, redness, swelling, or discharge from the nail. If the infection spreads to the surrounding skin, it can lead to more severe complications, such as cellulitis or a systemic infection.
Nail infections are often caused by fungi, bacteria, or yeast. They can enter the nail through small cuts, injuries, or even from contaminated objects like towels or nail clippers. Poor hygiene, damp environments, and weakened immune systems can also contribute to the development of nail infections.
Maintaining good nail hygiene is essential. Keep your nails clean and dry, trim them regularly, and avoid sharing personal items like nail clippers or towels. Ensure you wear protective gloves when engaging in activities that may expose your hands to moisture or chemicals. If you have a history of nail infections, consider using antifungal nail products as a preventive measure.
In severe cases, a nail infection can lead to the nail becoming thickened, discolored (yellow, brown, or black), and brittle. The surrounding skin may appear red, swollen, and painful. If the infection is left untreated, it can cause permanent nail damage, deformity, and even spread to other parts of the body.
Treatment options depend on the underlying cause and severity of the infection. Antifungal medications, either topical or oral, are commonly prescribed. In some cases, surgical intervention may be required to remove the infected portion of the nail or to drain any accumulated pus. Proper nail care and hygiene practices are crucial during and after treatment to prevent recurrence.







