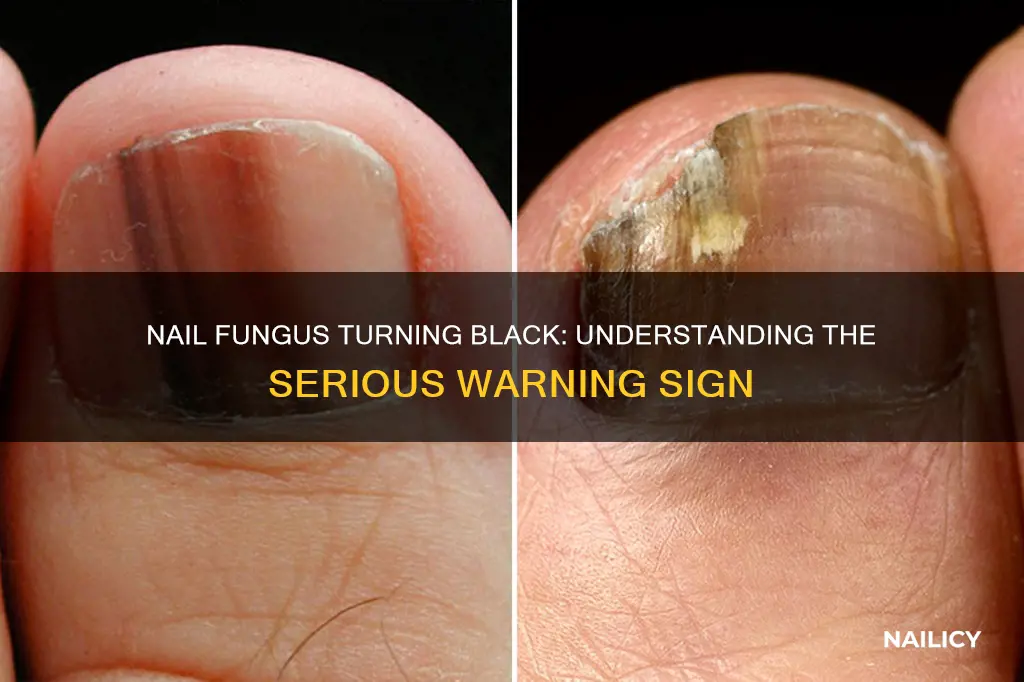
Nail fungus, a common yet often overlooked condition, can manifest in various ways, and one of the most concerning signs is the appearance of blackened areas on the nails. This darkening of the nail can be a cause for concern and may indicate a more severe or advanced infection. Understanding the reasons behind this change in color is crucial for timely intervention and treatment. When nail fungus turns black, it often signifies a progression of the infection, which can lead to more serious health complications if left untreated. This paragraph aims to explore the significance of this transformation and its implications for individuals affected by this condition.
What You'll Learn
- Nail Plate Damage: Blackened areas indicate potential nail plate damage, often due to prolonged fungal infection
- Oxygen Deprivation: Fungus thrives in low-oxygen environments, leading to blackened spots as a result of oxygen deprivation
- Skin Cell Buildup: Blackened areas may result from excessive skin cell buildup, a common symptom of nail fungus
- Nail Bed Infection: Blackened spots can be a sign of a deeper nail bed infection, requiring prompt treatment
- Viral Overlap: Blackened areas may overlap with viral infections, complicating diagnosis and treatment

Nail Plate Damage: Blackened areas indicate potential nail plate damage, often due to prolonged fungal infection
Nail fungus, a common yet often overlooked condition, can manifest in various ways, and one of the most concerning signs is the appearance of blackened areas on the nail plate. This darkening of the nail can be a cause for concern and may indicate a more severe and prolonged fungal infection. When a fungal infection takes hold of the nail, it can lead to significant damage, and the blackened regions are a visual indicator of this damage.
The nail plate, a hard protective layer covering the nail bed, is crucial for the overall health of the nail. When a fungal infection persists, it can penetrate the nail plate, causing it to become discolored and distorted. The blackened areas are often a result of the infection's impact on the nail's structure and the subsequent breakdown of the nail plate. This breakdown can lead to a range of issues, including thickening, brittleness, and even the nail lifting away from the nail bed.
Prolonged fungal infections are a significant concern as they can lead to permanent nail damage. The blackened regions are a sign that the infection has progressed and may have caused irreversible changes to the nail plate. Over time, the affected nail may become discolored, thickened, and prone to breakage, affecting both the appearance and functionality of the nail. It is essential to address this issue promptly to prevent further complications.
If you notice blackened areas on your nails, it is crucial to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can provide a proper diagnosis, which may involve a visual examination and, in some cases, a nail culture to identify the specific fungus causing the infection. Early detection and treatment are vital to managing nail fungus effectively and preventing long-term damage. Treatment options can include antifungal medications, topical treatments, or even surgical interventions in severe cases.
In summary, blackened areas on the nail plate are a critical sign of potential nail plate damage caused by a prolonged fungal infection. Recognizing this symptom early and seeking appropriate medical care is essential to preserving nail health and preventing further complications. With timely intervention, individuals can effectively manage nail fungus and restore the integrity of their nails.
Unraveling the Mystery: Corrosion of the Fingernails Explained
You may want to see also

Oxygen Deprivation: Fungus thrives in low-oxygen environments, leading to blackened spots as a result of oxygen deprivation
Nail fungus, a common yet often unsightly condition, can manifest in various ways, and one of the more concerning presentations is when the fungus turns black. This darkening of the nail can be a sign of a more severe infection and may indicate a progression of the disease that requires prompt attention. One of the primary reasons for this transformation is related to the unique environment within the nail bed.
The nail bed, a confined and often moist space, provides an ideal habitat for fungi. When an infection takes hold, it can quickly adapt to the low-oxygen conditions present in this area. Fungi, including those that cause nail infections, are aerobic organisms, meaning they require oxygen to survive and reproduce. However, in the confined space of the nail bed, oxygen levels are naturally low due to poor circulation and the limited space for gas exchange. This low-oxygen environment becomes a breeding ground for the fungus, allowing it to thrive and multiply rapidly.
As the fungus proliferates, it can lead to a buildup of metabolic waste products, including those that are toxic to the surrounding tissues. These toxins can cause the death of healthy cells and the darkening of the nail. The blackened spots are often a result of the breakdown of proteins and other cellular components, which can lead to the release of iron-rich compounds that give the nail a dark color. This process is similar to what occurs in other fungal infections, such as those affecting the skin, where the presence of iron and the low-oxygen environment contribute to the characteristic darkening.
Understanding the role of oxygen deprivation in nail fungus is crucial for effective treatment. By recognizing that the fungus's ability to survive and spread is closely tied to the low-oxygen conditions, healthcare professionals can employ targeted therapies. Treatment options may include antifungal medications, which can be administered topically or orally, depending on the severity of the infection. Additionally, improving circulation and oxygen supply to the nail bed through proper foot care and, in some cases, medical interventions, can help create an environment less conducive to fungal growth.
In summary, the blackening of nail fungus is a result of the fungus's adaptation to low-oxygen environments within the nail bed. This adaptation allows the fungus to thrive and spread, leading to the darkening of the nail. Recognizing this relationship between oxygen deprivation and fungal growth is essential for effective treatment, ensuring that patients receive the necessary care to address this often-disabling condition.
Unraveling the Mystery: What Do Dark Red Nails Symbolize?
You may want to see also

Skin Cell Buildup: Blackened areas may result from excessive skin cell buildup, a common symptom of nail fungus
Nail fungus, a common and often persistent condition, can present itself in various ways, and one of the more concerning manifestations is the appearance of blackened areas on the nail. This darkening of the nail can be a sign of an underlying fungal infection, which, if left untreated, can lead to further complications and potential health risks. Understanding the causes and implications of this symptom is crucial for timely intervention and management.
One of the primary reasons for nail fungus turning black is the presence of excessive skin cell buildup. Our nails are made up of a combination of proteins, including keratin, which is also found in hair and skin. When a fungal infection takes hold, it can disrupt the normal growth and shedding of these skin cells. As a result, the affected area may experience rapid cell division, leading to an overproduction of skin cells. This buildup can create a dark, discolored appearance, often described as a black or dark brown hue.
This excessive skin cell accumulation is a natural response to the body's attempt to protect itself from the fungal invasion. The immune system may trigger an inflammatory response, causing the affected area to become swollen and discolored. Over time, if the fungus persists, the continuous cycle of skin cell production and accumulation can lead to the darkening of the nail. It is important to note that this process is not unique to nail fungus and can occur with other types of infections or even due to certain medications.
The blackened areas on the nails are often a result of the body's attempt to seal off the infected area, creating a barrier to prevent the spread of the fungus. This sealing process can lead to the accumulation of dead skin cells, resulting in the dark color. In some cases, the fungus may also produce pigments that contribute to the blackening. It is a complex process that highlights the body's defense mechanisms and the challenges posed by fungal infections.
Treating nail fungus and addressing the underlying cause of excessive skin cell buildup is essential. This may involve antifungal medications, either in the form of topical treatments or oral prescriptions. Proper nail care, including regular trimming and cleaning, can also help manage the condition. Seeking professional medical advice is crucial to determine the appropriate treatment plan, especially when dealing with persistent or severe nail fungus infections.
Unraveling the Mystery: Vertical Ridge Nail Signs
You may want to see also

Nail Bed Infection: Blackened spots can be a sign of a deeper nail bed infection, requiring prompt treatment
Nail fungus, a common yet often overlooked condition, can manifest in various ways, and one of the most concerning signs is the appearance of blackened spots on the nail. This darkening of the nail can be a critical indicator of a more severe and potentially harmful infection. When a nail fungus progresses to this stage, it is essential to understand the implications and take immediate action to prevent further complications.
The blackened spots on the nail are not merely a cosmetic concern but a sign of an infection that has reached the nail bed. This infection is often caused by a type of fungus called dermatophytes, which can thrive in warm and moist environments, such as public showers, pools, or even shared towels and socks. When these fungi penetrate the nail, they can lead to a condition known as onychomycosis, which is a fungal infection of the nail. As the infection advances, it may cause the nail to become discolored, and in some cases, it can result in the darkening and thickening of the nail plate.
The nail bed, a delicate and vital part of the nail structure, is responsible for the nail's growth and health. When an infection sets in, it can lead to inflammation and damage to this area. Blackened spots often indicate that the infection has spread to the deeper layers of the nail bed, causing irritation and potential pain. If left untreated, this deeper infection can lead to permanent damage to the nail and even bone loss in severe cases.
Prompt treatment is crucial when dealing with a nail bed infection. Over-the-counter antifungal medications can be an initial step, but for more severe cases, a podiatrist or dermatologist may prescribe stronger antifungal drugs, either in the form of oral medications or topical treatments. In some instances, the affected nail may need to be partially or completely removed to allow for better treatment and prevent the spread of the infection. Proper foot hygiene, including keeping the feet clean and dry, and wearing breathable shoes, can also help prevent and manage nail fungus.
In summary, the appearance of blackened spots on a nail should not be ignored, as it may signify a serious nail bed infection. Early intervention is key to preventing the infection from spreading and causing long-term damage. If you suspect a nail fungus or notice any unusual changes in your nails, seeking professional medical advice is essential to ensure appropriate treatment and maintain overall foot health.
Mastering the Art of Flirting: Understanding 'Nailing a Girl
You may want to see also

Viral Overlap: Blackened areas may overlap with viral infections, complicating diagnosis and treatment
Nail fungus, a common condition affecting the nails, can present various symptoms, and one of the more concerning manifestations is the appearance of blackened areas. This darkening of the nail can be a sign of a more complex and challenging condition, often overlapping with viral infections. When this occurs, the diagnosis and treatment process becomes intricate, requiring a comprehensive understanding of the underlying causes.
The blackened areas in the nails are typically a result of the infection spreading and affecting the deeper layers of the nail structure. This can happen when a fungal infection, often caused by dermatophytes or yeasts, progresses and invades the nail bed and surrounding tissues. As the infection advances, it may lead to the formation of dark, discolored patches, which can be mistaken for other nail disorders.
Viral infections can also cause similar symptoms, making the identification of the exact cause challenging. Viral nail infections, such as those caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) or herpes simplex virus (HSV), can lead to changes in the nail's appearance, including discoloration. In some cases, these viral infections may coexist with a fungal infection, creating a complex clinical picture. For instance, a patient might present with a blackened area due to a fungal infection, only to discover that a concurrent viral infection is also present, further complicating the treatment approach.
Diagnosing this overlap requires a meticulous examination and a comprehensive medical history. Healthcare professionals must consider the patient's overall health, recent illnesses, and potential exposure to fungi or viruses. A detailed physical examination, including a thorough inspection of the nails, skin, and mucous membranes, is essential. Additionally, laboratory tests, such as nail clippings for fungal culture or viral DNA testing, can aid in confirming the presence of both fungal and viral infections.
Treating this complex scenario requires a multifaceted approach. Antifungal medications are often the first line of treatment for nail fungus, but their effectiveness may be reduced when a viral infection is also present. In such cases, antiviral drugs may be necessary to address the viral component. Combining these treatments and ensuring they are tailored to the specific infections involved is crucial for successful management. Moreover, patient education about proper nail hygiene, regular trimming, and the importance of completing the full course of treatment is vital to prevent recurrence and minimize the risk of viral overlap.
Unraveling the Meaning Behind Nine Inch Nails
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
When nail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, progresses, it can lead to a darkening of the nail plate. This darkening is often due to the infection spreading deeper into the nail bed, causing an increase in melanin production. Melanin is a pigment that gives color to the skin, hair, and nails, and its overproduction can result in a dark, discolored appearance.
Treating blackened nail fungus typically involves a combination of antifungal medications. These can be administered topically, orally, or even through laser therapy. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional or a podiatrist for an accurate diagnosis and to determine the most suitable treatment plan. Early intervention is crucial to prevent the infection from spreading further.
Yes, nail fungus, including the blackened form, is contagious. It can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected person's nails, skin, or even contaminated surfaces. Sharing personal items like nail clippers or towels can also contribute to the spread of the infection. Proper hygiene and avoiding direct contact with infected individuals are essential to prevent the fungus from spreading.
While complete cure is possible, it may take a significant amount of time and effort. The treatment duration can vary depending on the severity of the infection and the individual's overall health. Maintaining good foot hygiene, keeping nails short, and using antifungal treatments as prescribed by a doctor can help manage and potentially cure the fungus. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are recommended to monitor progress and ensure the infection is under control.