Nail biting, also known as onychophagia, is a common nervous habit where an individual bites, sucks, or gnaws on their fingernails. This behavior can be a sign of anxiety, stress, or boredom, and often serves as a temporary coping mechanism for individuals to relieve tension or find comfort. It can lead to various health issues, including nail damage, infections, and even an increased risk of injury to the mouth and tongue. Understanding the underlying causes and potential consequences of nail biting is essential for developing effective strategies to manage and potentially stop this habit.
What You'll Learn
- Psychological Triggers: Biting nails often stems from stress, anxiety, or boredom
- Habit Formation: It can become a repetitive behavior, hard to break
- Social Implications: Nail biting may indicate nervousness or a lack of confidence
- Health Risks: Biting nails can lead to infections, tooth damage, and bad breath
- Alternative Therapies: Techniques like mindfulness or fidget toys can help reduce the habit

Psychological Triggers: Biting nails often stems from stress, anxiety, or boredom
Nail biting, a common nervous habit, is often an unconscious response to underlying psychological triggers. Stress, anxiety, and boredom are three key factors that can lead to this behavior. When individuals find themselves in stressful situations, their bodies may react instinctively, and nail biting can become a temporary coping mechanism. It provides a physical outlet for the tension and anxiety that one might feel, offering a sense of relief, even if it is only temporary. This habit can be particularly prevalent among students during exam periods or professionals facing high-pressure work environments.
Anxiety, a close companion to stress, also plays a significant role in nail biting. People experiencing anxiety disorders may use nail biting as a way to channel their nervous energy. It can be a learned behavior, often starting in childhood, and continuing into adulthood as a familiar response to anxious feelings. For some, the act of biting nails provides a sense of control and comfort, especially in social situations or when facing unfamiliar circumstances.
Boredom, while often associated with leisure time, can also trigger nail biting. When individuals are not engaged in meaningful activities, their minds may wander, leading to restlessness and a desire for stimulation. Biting nails can serve as a quick fix to alleviate this boredom, providing a temporary distraction from the lack of stimulation. This behavior can become a habit, especially if it is not addressed and replaced with healthier alternatives.
Understanding these psychological triggers is the first step towards breaking the habit. Recognizing the underlying causes allows individuals to develop strategies to manage stress, anxiety, and boredom more effectively. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, mindfulness practices, or engaging in hobbies and social activities can help reduce the urge to bite nails. By addressing the root causes, one can gradually replace this harmful habit with healthier coping mechanisms.
Unraveling the Mystery: Visualizing Nail Scratch Marks
You may want to see also

Habit Formation: It can become a repetitive behavior, hard to break
Finger nail biting is a common habit that many people engage in, often without even realizing it. It is a repetitive behavior that can become a hard-to-break habit, and understanding its underlying causes is essential for those looking to overcome this issue. This habit often stems from a combination of psychological and environmental factors. For some, it provides a temporary sense of comfort or anxiety relief, acting as a self-soothing mechanism. Others might bite their nails when they are bored, stressed, or even as a way to socialize, as it can be a shared activity among friends. The act of biting can be a learned behavior, especially during childhood, where it might have been encouraged or not addressed properly. Over time, the behavior becomes automatic, and the individual may not even be aware of the habit until it is brought to their attention.
The repetitive nature of nail biting is a significant challenge. It is a simple, accessible action that provides immediate gratification, making it a go-to response for many when they feel the urge to do so. The habit can be particularly difficult to break because it often serves as a coping mechanism, especially in stressful situations. For example, a student might bite their nails before an exam, or an office worker might do so during a stressful meeting. The habit can become a ritual, and breaking it might require addressing the underlying causes and finding alternative, healthier ways to manage stress and anxiety.
To overcome this habit, one must first identify the triggers. Keeping a journal can help in this regard, recording the times, places, and emotions associated with the behavior. Once the triggers are identified, one can work on developing healthier coping strategies. For instance, when feeling anxious, one could try deep breathing exercises or go for a short walk instead. It is also beneficial to understand the psychological aspects; for some, it might be a way to gain control or a sense of comfort, so exploring these feelings and finding alternative ways to address them is key.
Breaking the habit of nail biting requires a multi-faceted approach. It can be helpful to keep your nails short, as this removes the physical ability to bite. Additionally, finding substitutes like chewing gum or sucking on a straw can provide a similar sensory experience without the negative consequences. Social support is also crucial; sharing your goal with friends and family can provide accountability and encouragement. They can help keep you motivated and remind you of the benefits of a nail-biting-free life. Lastly, understanding that it might take time and patience is essential. Habits are hard to break, and relapses may occur, but with persistence and a commitment to healthier alternatives, it is definitely achievable.
Uncovering the Expert: Who Performs Finger Nail Surgery?
You may want to see also

Social Implications: Nail biting may indicate nervousness or a lack of confidence
Nail biting, a common habit for many, often goes unnoticed but can have significant social implications. It is a behavior that can reveal underlying emotions and behaviors, particularly when it comes to social interactions and one's overall confidence. This habit, while seemingly trivial, can provide insights into an individual's mental state and how they perceive themselves in social settings.
One of the primary social implications of nail biting is its association with nervousness. When an individual bites their nails, it often occurs in moments of anxiety or stress. This action can be a physical manifestation of a person's inability to express their nervousness verbally. For example, a student preparing for an exam might find themselves biting their nails as a coping mechanism, indicating a sense of unease and a need for reassurance. In social situations, this behavior can be observed when a person is about to speak in front of a group or engage in a potentially challenging conversation, suggesting a lack of confidence and a tendency to rely on nervous habits.
The act of nail biting can also reflect a person's overall level of self-assurance. Individuals who frequently bite their nails might be more prone to self-doubt and a lack of self-worth. This behavior can become a ritualistic response to social pressures and the fear of judgment. For instance, a person might bite their nails before a job interview, indicating a deep-rooted anxiety about their performance and the potential for rejection. Over time, this habit can reinforce a cycle of negative thoughts, making social interactions more challenging and potentially impacting an individual's ability to form and maintain relationships.
In social contexts, nail biting can be a subtle yet powerful indicator of an individual's emotional state. It may suggest that a person is uncomfortable in their own skin or is struggling with self-acceptance. This behavior can be particularly noticeable in situations where one's hands are visible, such as during a meeting or a social gathering. Observing someone else bite their nails in these situations could provide a clue about their underlying social anxieties or insecurities.
Understanding the social implications of nail biting can encourage individuals to reflect on their habits and the potential triggers. It highlights the importance of being mindful of one's body language and the messages it conveys to others. By recognizing these behaviors, people can take steps to manage their anxiety and build confidence, ultimately improving their social interactions and overall well-being.
Fungal Nail Care: The Specialist's Guide to Treatment and Prevention
You may want to see also

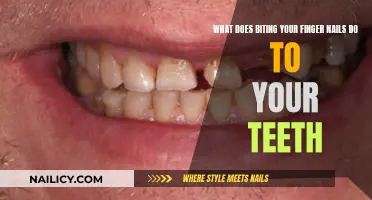
Health Risks: Biting nails can lead to infections, tooth damage, and bad breath
Nail biting, a common habit for many, involves the act of gnawing or chewing on one's fingernails. While it may provide temporary relief or a source of comfort, this seemingly harmless behavior can have significant health implications. One of the primary concerns associated with nail biting is the increased risk of infections. The human mouth is home to numerous bacteria, and when individuals bite their nails, they introduce these bacteria into their bloodstream. This can lead to various infections, including bacterial and fungal infections, which may affect not only the nails but also the surrounding skin and tissues. In some cases, these infections can become severe and may require medical intervention.
Tooth damage is another potential consequence of nail biting. The constant pressure and force exerted on the teeth while biting can cause enamel erosion, leading to sensitivity, pain, and even tooth decay. Over time, this habit can result in misaligned teeth and bite issues, requiring extensive dental work to correct. Moreover, the act of nail biting can contribute to bad breath, a condition known as halitosis. When nails are bitten, small pieces of nail debris and saliva can accumulate in the mouth, creating an environment conducive to bacterial growth. This bacterial overgrowth can lead to unpleasant odors, affecting not only the breath but also the overall oral hygiene.
The risks associated with nail biting extend beyond the mouth and teeth. In rare cases, chronic nail biting can lead to a condition called 'onychophagia,' which may result in the formation of calluses and corns on the fingertips. These complications can cause discomfort and pain, especially during physical activities. Additionally, the introduction of bacteria and other microorganisms through nail biting can have systemic effects, potentially leading to more severe health issues.
To mitigate these health risks, it is essential to address the habit of nail biting. Breaking this habit can be challenging, but various strategies can help. These include keeping your nails trimmed, using nail hardeners or covers, finding alternative stress-relieving activities, and seeking support from friends or professionals. By understanding the potential health consequences, individuals can make informed decisions to protect their overall well-being.
The Enigmatic Lesbian with the Long-Nail Mystery
You may want to see also

Alternative Therapies: Techniques like mindfulness or fidget toys can help reduce the habit
Nail biting, also known as onychophagia, is a common habit where individuals repeatedly bite, suck, or chew on their fingernails. It is a nervous habit that can have both psychological and physical implications. While it may provide temporary relief or a sense of comfort, it can lead to various health issues, including damaged nails, skin irritation, and an increased risk of infection. For those looking to break free from this habit, exploring alternative therapies and techniques can be a powerful approach.
One effective alternative therapy is mindfulness, a practice that encourages individuals to focus on the present moment and observe their thoughts and feelings without judgment. By applying mindfulness to nail biting, one can become more aware of the triggers and impulses that lead to the habit. For instance, when you feel the urge to bite your nails, take a moment to pause and notice the sensation. Instead of immediately giving in to the urge, try to observe the feeling as an object of awareness. Mindfulness meditation techniques, such as deep breathing or body scans, can help individuals develop a heightened sense of self-awareness, allowing them to recognize the habit and make conscious choices to stop.
Another useful tool in combating nail biting is the use of fidget toys. These are small, tactile objects designed to keep your hands occupied and provide a safe outlet for nervous energy. Fidget toys come in various forms, such as stress balls, spinning tops, or even more specialized tools like nail biting deterrents. By having a fidget toy readily available, you can redirect your focus and energy away from your nails. For example, when you feel the urge to bite, squeeze a stress ball or twist a fidget toy instead. Over time, the association between the habit and the relief it provides will weaken, making it easier to break the nail-biting habit.
Additionally, incorporating relaxation techniques into your daily routine can significantly reduce nail-biting episodes. Deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or even simple activities like yoga or tai chi can help calm the mind and body. When you feel stressed or anxious, these techniques can provide a healthy outlet for tension release, reducing the likelihood of nail biting. For instance, before a stressful event or meeting, take a few minutes to practice deep breathing, focusing on slow, controlled breaths. This can help lower anxiety levels and provide a sense of control, making it less appealing to resort to nail biting as a coping mechanism.
In summary, nail biting is a common habit that can be addressed through various alternative therapies and techniques. Mindfulness practices enhance self-awareness, allowing individuals to recognize and manage their nail-biting impulses. Fidget toys offer a safe and engaging alternative to channel nervous energy. Furthermore, incorporating relaxation techniques and stress management strategies into daily life can significantly contribute to reducing the habit. By exploring these alternative approaches, individuals can effectively break free from nail biting and develop healthier habits.
Unraveling the Mystery: Nail Biting's Impact on Your Teeth
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Nail biting, also known as onychophagia, is a common habit where an individual bites, sucks, or gnaws on their nails or the skin around them. It is often an unconscious behavior and can be a nervous tic or a coping mechanism to deal with stress, anxiety, or boredom.
While nail biting itself is not typically a cause for major concern, it can be indicative of underlying emotional or psychological issues. It may be a symptom of anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), or other mental health conditions. If nail biting is accompanied by other concerning behaviors or affects daily life, it's advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
Yes, nail biting can sometimes be associated with low self-esteem or a lack of self-confidence. It may provide a temporary sense of comfort or distraction from negative thoughts or feelings. However, it's important to note that this behavior can become a harmful habit and may require addressing the root causes of low self-esteem.
Breaking the habit of nail biting can be challenging but is possible with various strategies. Some effective methods include:
- Identifying triggers and finding alternative ways to cope with stress or boredom.
- Keeping nails trimmed short to reduce the urge to bite.
- Using bitter-tasting nail polish or nail biting deterrents.
- Practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or engaging in hobbies to distract the mind.
- Seeking support from friends, family, or a therapist to stay motivated and accountable.