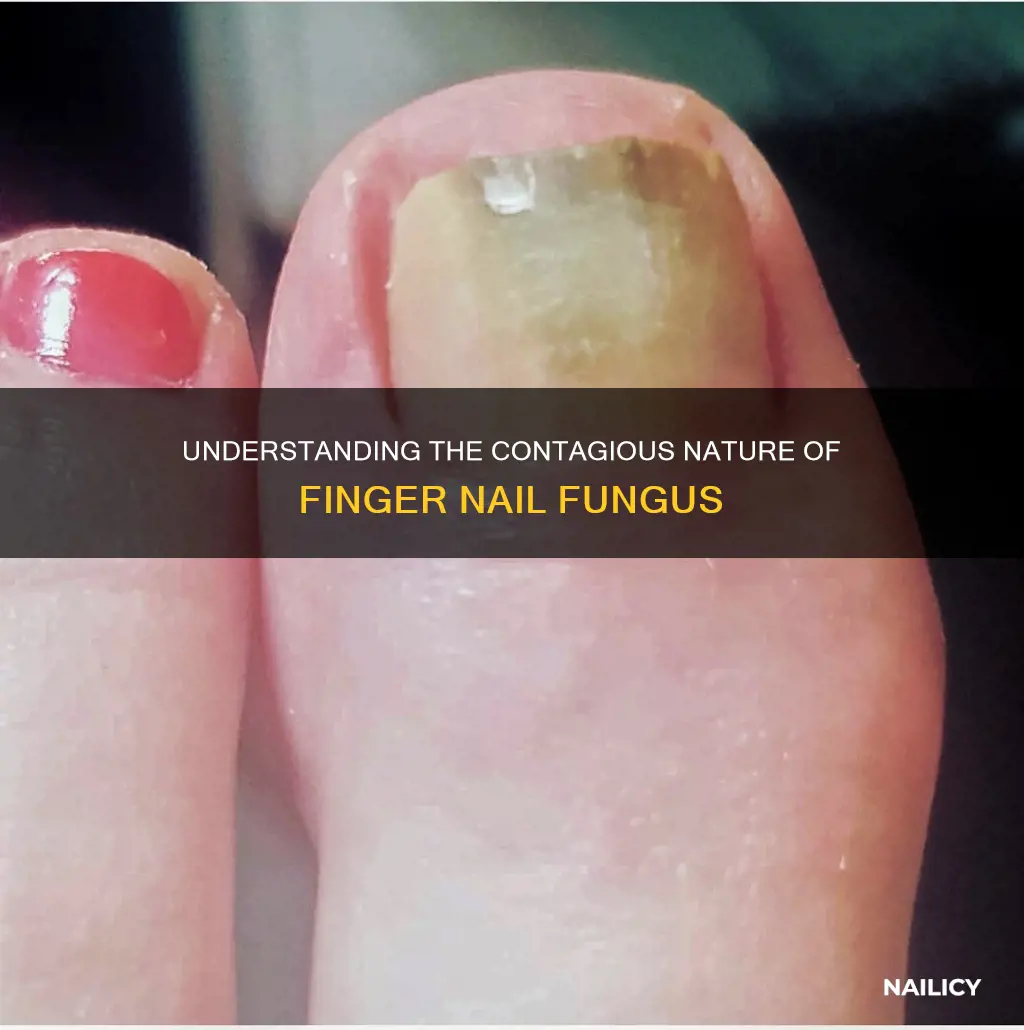
Finger nail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is a common condition that affects the nails, often causing discoloration, thickening, and brittleness. It can be a frustrating and persistent issue for many individuals. One common question regarding this condition is whether it is contagious. Understanding the contagious nature of finger nail fungus is essential for proper management and prevention. In this paragraph, we will explore the factors that determine the contagiousness of this fungal infection and provide insights into how it spreads and who is most at risk.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Fungal infections of the nails, often caused by dermatophytes, yeasts, or molds. |
| Contagiousness | Yes, certain types of nail fungus can be contagious, especially those caused by fungi that thrive in warm, moist environments like public showers, pools, and locker rooms. |
| Transmission | Direct contact with an infected person's nails or skin, or through contact with contaminated surfaces or objects. |
| Risk Factors | Sharing personal items like nail clippers, towels, or socks with an infected individual; having a weakened immune system; poor hygiene; and living in humid or warm climates. |
| Symptoms | Thickening, discoloration (white, yellow, or brown), brittleness, and separation of the nail from the nail bed. |
| Treatment | Antifungal medications (oral or topical), nail care routines, and lifestyle changes. |
| Prevention | Practicing good foot and nail hygiene, keeping nails short and clean, avoiding walking barefoot in public areas, and using antifungal products. |
What You'll Learn
- Transmission: Fungal infections can spread through direct contact or contaminated surfaces
- Risk Factors: Certain factors like weakened immune systems or moist environments increase susceptibility
- Symptoms: Nail discoloration, thickening, and brittleness are common signs of infection
- Treatment: Options include antifungal medications, topical treatments, and lifestyle changes
- Prevention: Keep nails clean, dry, and trimmed to reduce the risk of infection

Transmission: Fungal infections can spread through direct contact or contaminated surfaces
Fungal infections, including those affecting the nails, can indeed be contagious and easily transmitted from person to person. Understanding the modes of transmission is crucial for preventing the spread of these infections and maintaining good foot and nail health. One primary method of transmission is through direct contact with an infected individual or their contaminated items. This can occur when you come into physical contact with someone who has a fungal infection, such as sharing towels, socks, or shoes. The fungi responsible for these infections, such as dermatophytes, can survive on surfaces and fabrics, making it easy for them to be transferred. For instance, if an infected person uses a nail clipper or file, the fungi can remain on these tools, and if another person uses them without proper sanitization, they risk contracting the infection.
Another common way fungal infections spread is through contaminated surfaces and environments. Public areas like swimming pools, showers, locker rooms, and nail salons can be breeding grounds for these fungi. The moist and warm conditions in these settings provide an ideal environment for fungi to thrive and multiply. When an infected individual walks barefoot in these areas, they can leave behind fungal spores, which can then be tracked onto towels, floors, and other surfaces. If someone else comes into contact with these contaminated areas, they may inadvertently pick up the fungi, leading to an infection. It's important to note that fungi can also be transmitted through indirect contact, such as touching surfaces that an infected person has touched, and then touching your own mouth, nose, or eyes.
To prevent the spread of fungal nail infections, it is essential to practice good hygiene and take certain precautions. Always wear sandals or flip-flops in public showers, pools, and locker rooms to reduce direct contact with potential fungal sources. Ensure that you clean and disinfect nail tools, such as clippers and files, after each use, especially if they have been used by someone with a fungal infection. Additionally, encourage open communication about nail health within your social circles to promote awareness and reduce the risk of transmission through direct contact.
In summary, fungal nail infections can be contagious and are primarily transmitted through direct contact with infected individuals or their belongings, as well as indirect contact with contaminated surfaces. By understanding these transmission methods, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves and others from these common infections. Simple preventive measures can go a long way in maintaining a healthy environment and ensuring that fungal nail infections do not spread unnecessarily.
Unraveling the Mystery: Why Your Nails Form Ripples
You may want to see also

Risk Factors: Certain factors like weakened immune systems or moist environments increase susceptibility
Fungal infections, including those affecting the nails, can be a common concern for many individuals. When it comes to finger nail fungus, understanding the risk factors is crucial in preventing and managing this condition. One significant aspect to consider is the impact of a weakened immune system. Individuals with compromised immune systems, whether due to underlying health conditions or treatments like chemotherapy, are more susceptible to fungal infections. The body's natural defense mechanisms are impaired, making it easier for fungi to invade and establish an infection. For example, those with diabetes, HIV/AIDS, or autoimmune disorders may have a higher risk of developing nail fungus due to their weakened immune response.
Moist and humid environments also play a pivotal role in the development and spread of nail fungus. Fungi thrive in warm and damp conditions, making certain settings more conducive to their growth. Public areas like swimming pools, locker rooms, and nail salons, where individuals often go barefoot, can be breeding grounds for fungi. Shared towels, shoes, or nail tools can further contribute to the transmission of fungal infections. It is essential to maintain good hygiene practices and take necessary precautions in such environments to minimize the risk.
Additionally, direct contact with infected individuals can lead to the spread of nail fungus. Close contact or sharing personal items with someone who has a fungal infection increases the likelihood of contracting the same condition. This is particularly relevant in family settings or among close friends. Proper education and awareness about the contagious nature of nail fungus can help individuals take preventive measures and reduce the risk of transmission.
Other factors that may contribute to the susceptibility of nail fungus include age, as older adults may have slower-growing nails, making it harder to detect infections. Additionally, certain occupations or activities that involve prolonged exposure to water or moisture, such as swimming instructors or gardeners, may have a higher risk. It is important to recognize these risk factors and take proactive steps to prevent and manage nail fungus effectively.
In summary, understanding the risk factors associated with finger nail fungus is essential for prevention and early intervention. Weakened immune systems and moist environments are key contributors to the development and spread of this fungal infection. By being aware of these factors and taking appropriate measures, individuals can significantly reduce their chances of contracting nail fungus and maintain healthy nails.
The Mystery of Penn Gillette's Red Nail: Unraveling the Story
You may want to see also

Symptoms: Nail discoloration, thickening, and brittleness are common signs of infection
Nail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is a common condition that affects the nails, often leading to discoloration, thickening, and brittleness. These symptoms are indicative of an infection caused by fungi, which can thrive in warm and moist environments, such as those found in shoes and socks. The condition can affect any nail, but it is more commonly observed in the toenails due to the nature of footwear and the increased exposure to moisture.
One of the most noticeable symptoms is nail discoloration. The affected nail may appear white, yellow, or brown, often with a fuzzy or discolored appearance. This discoloration is a result of the fungus invading the nail and altering its natural color. Over time, the affected nail can become thicker and more brittle, making it susceptible to breakage and splitting. The fungus feeds on the keratin present in the nail, causing it to weaken and change in texture.
Thickening of the nail is another prominent sign. As the infection progresses, the nail plate may become swollen and enlarged, making it difficult to trim or cut. This thickening can lead to discomfort and pain, especially when wearing shoes or engaging in activities that require manual dexterity. The affected nail may also become distorted in shape, losing its natural curvature and becoming abnormally curved or ridged.
Brittleness is a direct consequence of the fungal infection. The nail becomes fragile and prone to cracking or splitting, especially at the tips or sides. This brittleness can be further exacerbated by the thickening and discoloration of the nail, making it even more challenging to manage. In severe cases, the nail may lift or separate from the nail bed, leading to pain and potential infection.
It is important to note that nail fungus can be contagious, especially in environments where fungi thrive. Public showers, swimming pools, and locker rooms are common areas where the fungi can spread. If you suspect a fungal infection, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Early detection and treatment can help prevent the infection from spreading and causing further complications.
The Unseen Bond: Exploring the Connection Between Nails and Fingers
You may want to see also

Treatment: Options include antifungal medications, topical treatments, and lifestyle changes
Fungal nail infections, often referred to as onychomycosis, are indeed contagious and can spread through direct contact with an infected person or by touching contaminated surfaces. The fungus thrives in warm, moist environments, making public areas like swimming pools, showers, and locker rooms potential hotspots for transmission. Understanding the contagious nature of this condition is crucial for implementing effective treatment strategies.
When it comes to treatment, there are several options available to manage and eliminate the fungus. Antifungal medications are a common first-line treatment. These can be prescribed in the form of oral pills or topical creams and ointments. Oral antifungals are particularly effective for severe infections and may be recommended for those with extensive nail involvement. Topical treatments, such as antifungal nail paints or creams, are applied directly to the infected nail and surrounding skin. These are often used for milder cases or as an adjunct to oral medications.
In addition to medication, lifestyle changes play a significant role in managing and preventing the recurrence of fungal nail infections. Keeping the feet and nails clean and dry is essential. Regularly trimming and filing the nails can help improve air circulation and reduce the fungus's ability to thrive. Wearing breathable shoes and changing socks daily can also prevent moisture buildup, which is crucial in maintaining a healthy environment for the nails.
For more severe cases or when other treatments fail, medical professionals might recommend surgical interventions. This could involve the removal of the infected nail or parts of it to allow for better medication absorption and to prevent the fungus from spreading further. It is important to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and to determine the most suitable treatment plan.
In summary, treating finger nail fungus involves a combination of antifungal medications, topical treatments, and lifestyle modifications. Early intervention is key to successful management, and individuals should be aware of the contagious nature of the infection to take preventive measures and seek appropriate medical advice.
Nail Care: 3 Essential Tips for Healthy, Strong Fingernails
You may want to see also

Prevention: Keep nails clean, dry, and trimmed to reduce the risk of infection
Fungal infections, including those affecting the nails, can be contagious, especially in certain environments. Understanding the preventive measures is crucial to maintaining nail health and preventing the spread of these infections. One of the most effective ways to reduce the risk of nail fungus is by practicing good hygiene and adopting a few simple habits.
Keeping your nails clean is an essential part of this routine. Regularly wash your hands and feet with soap and warm water, ensuring that you thoroughly clean the areas around your nails. This practice helps eliminate any potential fungi or bacteria that may be present. Pay close attention to the spaces between your toes and fingers, as these areas can be breeding grounds for fungi. Use a nail brush to scrub your nails and the surrounding skin, ensuring a thorough clean.
Drying your hands and feet properly is another critical step. After washing, make sure to thoroughly dry them, especially between the toes and fingers. Moisture can create an ideal environment for fungi to thrive, so ensuring that your skin is completely dry is essential. Consider using a soft towel and gently patting your skin dry to avoid any friction that could cause irritation.
Trimming your nails regularly is a simple yet effective way to prevent nail fungus. Keep your nails short and well-maintained. Trim them straight across to avoid any sharp edges that could potentially catch and tear the skin. File the edges gently to create a smooth surface, which can help prevent ingrown nails and reduce the risk of infection. Regular trimming also allows for better air circulation around the nails, which is beneficial for overall nail health.
Additionally, it is advisable to use separate tools for nail care, especially if you or someone in your household has a fungal infection. This includes nail clippers, files, and brushes. Sharing personal care items can transfer fungi from one person to another, so maintaining individual tools is a good practice. By keeping your nails clean, dry, and trimmed, you significantly lower the chances of developing a fungal infection and contribute to overall better nail health.
Unveiling the Mystery: Why Your Nail Tips Turn White
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Nail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is a common fungal infection that primarily affects the toenails or fingernails. While it is not typically contagious in the traditional sense, meaning it cannot be easily transmitted from person to person through casual contact, it can be spread through shared items or environments. For example, walking barefoot in public showers or swimming pools can expose your feet to the fungus. Additionally, sharing personal items like nail clippers or towels with an infected individual can also contribute to the spread.
Nail fungus often enters the body through small cuts, cracks, or injuries on the skin surrounding the nails. These openings provide an entry point for fungi, which are commonly found in warm, moist environments like showers, locker rooms, and swimming pools. Fungi can also be contracted from contaminated objects, such as nail files, clippers, or shoes worn by an infected person.
There is no scientific evidence to suggest that nail fungus can be transmitted through sexual contact. Sexual transmission of fungi is rare and typically limited to specific types of fungi that are commonly found in warm, moist areas of the body, such as the skin folds and groin. Nail fungus is not one of them.
To reduce the risk of contracting nail fungus, it is recommended to practice good foot hygiene, including keeping your feet clean and dry, especially between the toes. Wear sandals or flip-flops in public showers and swimming pools, and avoid sharing personal items like nail clippers or towels. Additionally, maintaining a healthy immune system and keeping your nails clean and trimmed can help prevent fungal infections.







